Navigating the Skies: Corrosion Challenges in Aerospace and the Vital Role of Coating Inspector Courses
Introduction
The aerospace industry plays a crucial role in modern society, enabling global connectivity and transportation. However, with the advancements in technology and the increasing demands on aircraft, the industry faces significant challenges, one of which is corrosion. Corrosion can compromise the structural integrity of aircraft, leading to safety concerns and increased maintenance costs. In this context, the role of coating inspectors becomes paramount in ensuring the longevity and reliability of aerospace structures. This article delves into the corrosion challenges faced by the aerospace sector and emphasizes the vital role played by professionals who have undergone coating inspector courses.
Brief overview of corrosion challenges in the aerospace industry
Corrosion poses a persistent threat to aircraft components due to the harsh environmental conditions they endure, such as exposure to high altitudes, varying temperatures, and atmospheric pollutants. The primary materials used in aerospace, including aluminum and steel alloys, are susceptible to corrosion, which can manifest in the form of rust, pitting, or stress corrosion cracking. Moreover, aircraft are frequently subjected to diverse operational environments, from humid coastal regions to arid deserts, intensifying the corrosion risk. The aerospace industry’s commitment to safety and reliability necessitates proactive measures to mitigate corrosion effects.
Corrosion can weaken structural elements, compromise aerodynamic performance, and increase fuel consumption. To counteract these detrimental effects, aerospace engineers and maintenance professionals employ advanced coating technologies as a preventive measure. Coatings act as a protective barrier, shielding aircraft surfaces from corrosive elements and extending their operational lifespan.
This intricate battle against corrosion underscores the significance of trained coating inspectors. These professionals are equipped with the knowledge and skills gained from specialized courses, enabling them to assess coating quality, identify potential corrosion threats, and ensure compliance with industry standards. As we delve deeper into the role of coating inspectors, their expertise emerges as a linchpin in maintaining the structural integrity and safety of aerospace vehicles.
Importance of corrosion control in maintaining structural integrity and safety
Corrosion poses a significant threat to the structural integrity and safety of aerospace components, making effective corrosion control measures paramount. In the demanding environment of aviation, where aircraft are exposed to harsh weather conditions, high-altitude operations, and diverse atmospheric elements, corrosion can compromise the integrity of critical components such as wings, fuselage, and engine parts. This deterioration not only affects the overall performance of the aircraft but also jeopardizes passenger safety.
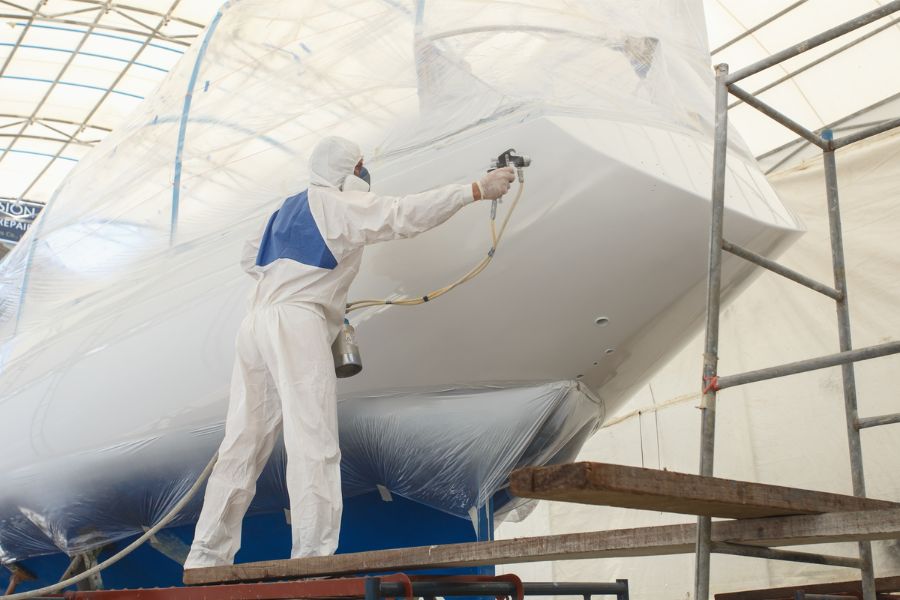
Corrosion control is essential to prevent the degradation of metals used in aircraft construction. Structural elements weakened by corrosion may fail under stress, leading to catastrophic consequences. To mitigate these risks, the aerospace industry employs a range of corrosion-resistant materials and coatings. These protective coatings act as a barrier between the metal substrate and environmental factors, preventing corrosion from taking hold. The effectiveness of these coatings, however, relies heavily on the precision and quality of application, making the role of coating inspectors crucial in ensuring their efficacy.
Introduction to the role of Coating Inspectors in addressing corrosion issues
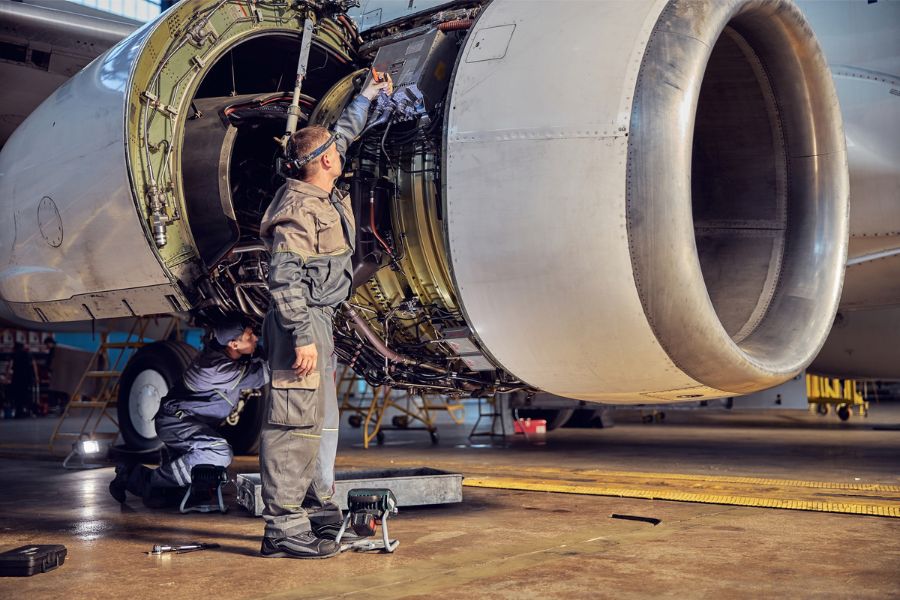
Coating inspectors play a pivotal role in the aerospace industry by ensuring the proper application and maintenance of protective coatings on aircraft components. These professionals are tasked with monitoring and evaluating coating systems to detect any signs of corrosion, coating failure, or defects. The role involves a combination of technical expertise and practical knowledge in coating technologies, surface preparation, and inspection techniques.
Coating inspectors are instrumental in guaranteeing that aerospace structures adhere to industry standards and regulations. By conducting thorough inspections, they identify potential corrosion risks and address them before they escalate. This proactive approach not only preserves the structural integrity of aircraft but also extends their operational lifespan, resulting in substantial cost savings for airlines and manufacturers.
In the context of the aerospace industry, where safety is paramount, coating inspectors contribute directly to risk mitigation. Through regular inspections and assessments, they contribute to the development of preventive maintenance strategies, ensuring that corrosion is identified and treated in its early stages. Coating inspector courses, therefore, play a vital role in equipping professionals with the skills and knowledge needed to perform these critical tasks. These courses cover topics such as coating application techniques, inspection methodologies, and the latest advancements in coating technologies.
Pain Points in Aerospace Corrosion Control
In the realm of aerospace engineering, corrosion poses a significant challenge that demands meticulous attention. The corrosive effects on aircraft and related components not only compromise structural integrity but also impact the overall safety and longevity of these sophisticated machines. The pain points in aerospace corrosion control are multifaceted, encompassing challenges in detection, prevention, and maintenance. From the intricate inner workings of engines to the exposed surfaces of the airframe, each component is susceptible to corrosion.
Coating inspectors play a pivotal role in addressing these pain points. Their expertise lies in scrutinizing coatings applied to aerospace materials, identifying potential vulnerabilities, and ensuring that protective layers are effectively shielding against corrosive elements. Through comprehensive training in coating inspector courses, professionals acquire the skills needed to navigate these challenges and contribute significantly to the robust corrosion control measures essential for the aviation industry.
Harsh Environmental Conditions
Aerospace systems operate in a diverse range of environmental conditions, exposing them to harsh elements such as saltwater, extreme temperatures, and atmospheric contaminants. These conditions accelerate the corrosion process, making it imperative to implement advanced protective measures. Coating inspectors specialize in evaluating the efficacy of protective coatings under these demanding circumstances.
By undergoing coating inspector courses, individuals gain insights into the specific challenges posed by harsh environments. From understanding the impact of UV radiation on coatings to evaluating the resilience of materials in corrosive atmospheres, coating inspectors are equipped to assess and address the vulnerabilities of aerospace components. Their role becomes particularly crucial in ensuring that coatings withstand the rigors of the skies, contributing to the overall durability and safety of aircraft.
Material Compatibility
Aerospace engineering involves the use of diverse materials, each with its own set of characteristics and vulnerabilities to corrosion. The compatibility between protective coatings and these materials is a critical aspect of corrosion control. Coating inspectors are trained to assess and ensure that the chosen coatings not only provide effective protection but also interact seamlessly with the underlying materials.
In coating inspector courses, emphasis is placed on understanding the chemical and physical properties of both coatings and aerospace materials. This knowledge enables inspectors to identify potential issues related to material compatibility, preventing situations where coatings may inadvertently exacerbate corrosion rather than mitigating it. The ability to navigate the intricate nuances of material-coating interactions is a hallmark of a skilled coating inspector, underscoring the vital role they play in aerospace corrosion control.
Maintenance Challenges
Aerospace maintenance is a complex and resource-intensive process. Traditional maintenance approaches often lead to extended downtime, increased costs, and operational disruptions. Corrosion-related maintenance challenges add an additional layer of complexity, as addressing corrosion issues requires precision and expertise.
Coating inspectors contribute significantly to overcoming maintenance challenges by conducting thorough assessments of the coating systems. Through their specialized training, they can recommend targeted interventions to address corrosion issues promptly. By identifying and rectifying coating deficiencies early on, these professionals play a crucial role in minimizing downtime and optimizing maintenance efforts, ultimately enhancing the overall efficiency of aerospace operations.
Solutions for Aerospace Corrosion Control
Aerospace structures are constantly exposed to harsh environmental conditions, making corrosion a significant challenge in the industry. This section explores the various solutions implemented for aerospace corrosion control. The first line of defense often involves the application of advanced coatings on aircraft surfaces. These coatings act as protective barriers, shielding the metal components from corrosive elements such as moisture, salt, and chemicals.
Among the notable solutions are corrosion-resistant alloys, cathodic protection systems, and environmental control measures. Corrosion-resistant alloys are engineered materials designed to withstand the corrosive effects of the aerospace environment. Cathodic protection involves sacrificial anodes or impressed currents to prevent corrosion by making the aircraft structure the cathode in a corrosion cell. Environmental control measures include the regulation of humidity and temperature within aircraft storage and maintenance facilities.
However, the efficacy of these solutions heavily relies on the quality and integrity of the applied coatings. This underscores the critical importance of trained professionals, specifically coating inspectors, in ensuring the longevity and performance of these protective coatings.
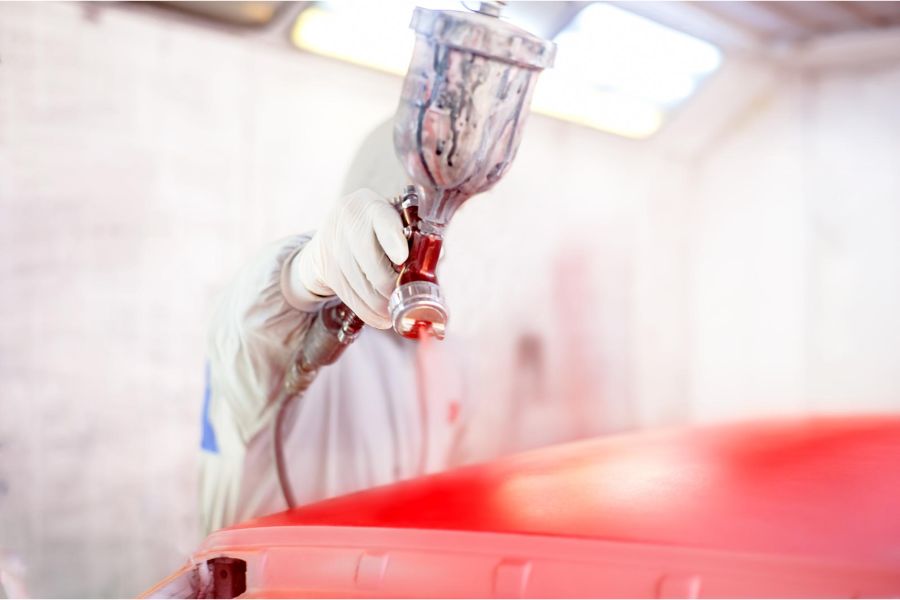
Advanced Coating Technologies
This section delves into the advancements in coating technologies that play a pivotal role in aerospace corrosion control. With constant innovation, coating technologies have evolved to meet the unique challenges posed by the aerospace environment. Advanced coatings go beyond mere protection; they enhance aerodynamics, reduce drag, and contribute to fuel efficiency.
Polymer matrix composites, ceramic coatings, and nanotechnology-based coatings are at the forefront of these advancements. Polymer matrix composites offer lightweight yet robust protection, ideal for aerospace applications where weight is a critical factor. Ceramic coatings provide high-temperature resistance, making them suitable for components exposed to extreme heat during flight. Nanotechnology-based coatings leverage microscopic particles to create ultra-thin, highly effective protective layers.
As these advanced coatings become more prevalent, the need for skilled coating inspectors becomes even more apparent. Coating inspectors play a vital role in ensuring that these cutting-edge technologies are applied correctly and meet the stringent quality standards required for aerospace applications.
Regular Inspections and Maintenance
A key aspect of corrosion control in aerospace is the implementation of regular inspections and maintenance protocols. Coating Inspectors play a pivotal role in this process, as they are trained to conduct thorough assessments of coated surfaces. These inspections are not only reactive but also preventive, aiming to identify early signs of corrosion or coating degradation before they escalate into more severe problems.
Coating Inspector courses emphasize the importance of systematic inspection methodologies, including visual assessments, non-destructive testing, and advanced analytical techniques. By staying proactive in their approach, Coating Inspectors contribute significantly to the overall maintenance strategies of aerospace entities, ensuring that any emerging corrosion issues are addressed promptly and effectively.
Improved Material Selection
Another critical element in the fight against aerospace corrosion is the careful selection of materials. Coating Inspectors, through their training, become well-versed in understanding the compatibility of coatings with various substrates and environmental conditions. This knowledge is instrumental in guiding aerospace engineers and manufacturers towards improved material selection for aircraft components.
Coating Inspector courses delve into the science behind material interactions and corrosion mechanisms, empowering professionals to make informed decisions during the design and manufacturing phases. The ultimate goal is to choose materials and coatings that not only enhance performance but also resist corrosion, thereby extending the lifespan of aerospace equipment.
Coating Inspector Courses and Their Relevance
Coating inspector courses play a pivotal role in addressing corrosion challenges within the aerospace industry. These courses are specifically designed to equip professionals with the knowledge and skills necessary to assess, monitor, and ensure the effectiveness of protective coatings on aircraft and aerospace components.
In essence, the relevance of coating inspector courses lies in their ability to combat the corrosive forces that aerospace materials face during their operational life. Corrosion poses a significant threat to the structural integrity and overall performance of aircraft, making it imperative to have qualified individuals who can inspect and assess coating systems.
These courses cover a spectrum of topics ranging from the science of corrosion to the latest advancements in coating technologies. Participants learn to identify various types of corrosion, understand the principles of different coating materials, and acquire hands-on experience in inspecting coatings for defects and vulnerabilities. The practical knowledge gained through these courses is directly applicable to real-world scenarios in aerospace maintenance and manufacturing.
As aviation standards become more stringent and aerospace materials evolve, the role of coating inspectors becomes increasingly critical. Professionals trained through these courses become instrumental in ensuring compliance with industry regulations, enhancing safety, and extending the lifespan of aircraft.
Overview of Coating Inspector Courses
Coating inspector courses provide a comprehensive overview of the principles, methodologies, and best practices related to protective coatings in the aerospace sector. These courses cater to a diverse audience, including technicians, engineers, and quality control personnel involved in the manufacturing, maintenance, and repair of aircraft. The curriculum typically covers fundamental aspects such as corrosion mechanisms, surface preparation techniques, coating application methods, and inspection protocols. Participants delve into the intricacies of different coating types, including primers, topcoats, and specialty coatings, understanding their unique properties and applications.
Theoretical components are complemented by practical training sessions where participants engage in hands-on exercises, simulating real-world scenarios. This practical exposure is crucial for honing the skills required to identify coating defects, assess adhesion, and determine the overall condition of protective coatings.
Moreover, coating inspector courses often incorporate the latest industry standards and regulations, ensuring that participants stay abreast of the dynamic aerospace landscape. This includes understanding the environmental and operational factors that contribute to corrosion, as well as exploring innovative coating technologies designed to mitigate these challenges.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the aerospace industry’s perpetual battle against corrosion underscores the critical importance of robust protective measures, with coating inspection emerging as a linchpin in this defense. Navigating the Skies: Corrosion Challenges in Aerospace and the Vital Role of Coating Inspector Courses encapsulates the pivotal role played by professionals trained in coating inspection. As aviation technology advances, so too do the challenges posed by corrosion, demanding a workforce equipped with the knowledge and skills to combat this persistent threat.
Coating inspectors, through specialized training courses, stand at the forefront of ensuring the durability and safety of aerospace components. One noteworthy institution addressing this need is the Corcon Institute of Corrosion, a beacon of excellence in offering comprehensive coating inspector courses. Their commitment to delivering high-quality education underscores the urgency and significance of producing skilled professionals adept at navigating the intricacies of corrosion control in aerospace. In essence, the success of the aerospace industry in mitigating corrosion hinges on the expertise instilled through institutions like Corcon, shaping a future where the skies are not just traversed but conquered with unwavering resilience.
FAQs
Q1: What are the primary materials in the aerospace industry susceptible to corrosion, and why is corrosion a significant concern?
Answer: The primary materials in aerospace, such as aluminum and steel alloys, are susceptible to corrosion due to exposure to harsh environmental conditions like high altitudes, varying temperatures, and atmospheric pollutants. Corrosion compromises structural integrity, aerodynamic performance, and increases maintenance costs, posing a serious threat to aircraft safety.
Q2: How do protective coatings contribute to aerospace corrosion control, and why is the role of coating inspectors crucial in this context?
Answer: Protective coatings act as a barrier, shielding aircraft surfaces from corrosive elements and extending operational lifespan. Coating inspectors, through specialized training, assess coating quality, identify potential corrosion threats, and ensure compliance with industry standards. Their expertise is pivotal in maintaining structural integrity and safety by addressing coating issues proactively.
Q3: Why is corrosion control essential in maintaining the structural integrity and safety of aerospace components?
Answer: Corrosion weakens structural elements, compromising the integrity of critical components like wings and fuselage. This degradation not only impacts overall aircraft performance but also poses a safety risk to passengers. Corrosion control measures, including advanced coatings and inspections by trained professionals, are crucial to prevent catastrophic consequences.
Q4: What challenges do aerospace engineers face in combating corrosion, and how do coating inspectors help address these challenges?
Answer: Aerospace engineers face challenges in harsh environmental conditions, material compatibility, and maintenance complexities. Coating inspectors specialize in scrutinizing coatings, identifying vulnerabilities, and ensuring effective protection. Their expertise contributes significantly to overcoming challenges, minimizing downtime, and optimizing maintenance efforts in the aerospace industry.
Q5: How do coating inspector courses contribute to the aerospace industry, and what topics do these courses cover?
Answer: Coating inspector courses equip professionals with the knowledge and skills to assess, monitor, and ensure the effectiveness of protective coatings. Topics covered include corrosion mechanisms, surface preparation, coating application methods, and inspection protocols. These courses are crucial in producing skilled individuals who play a vital role in maintaining compliance with industry standards, enhancing safety, and extending the lifespan of aircraft.
Image Reference: Freepik
Disclaimer: All trademarks, logos, and brand names are the property of their respective owners. All company, product, and service names used in this website are for identification purposes only. Use of these names, trademarks, and brands does not imply endorsement.